Posture and Pressure Care: Seat Choices That Protect the Back, Hips, and Skin
Proper seating is far more than just comfort—it’s a critical component of health and wellness that directly impacts spinal alignment, pressure distribution, and skin integrity. With millions of people spending extended periods seated daily, understanding how seat choices affect our bodies has become essential for preventing both immediate discomfort and long-term health complications.123

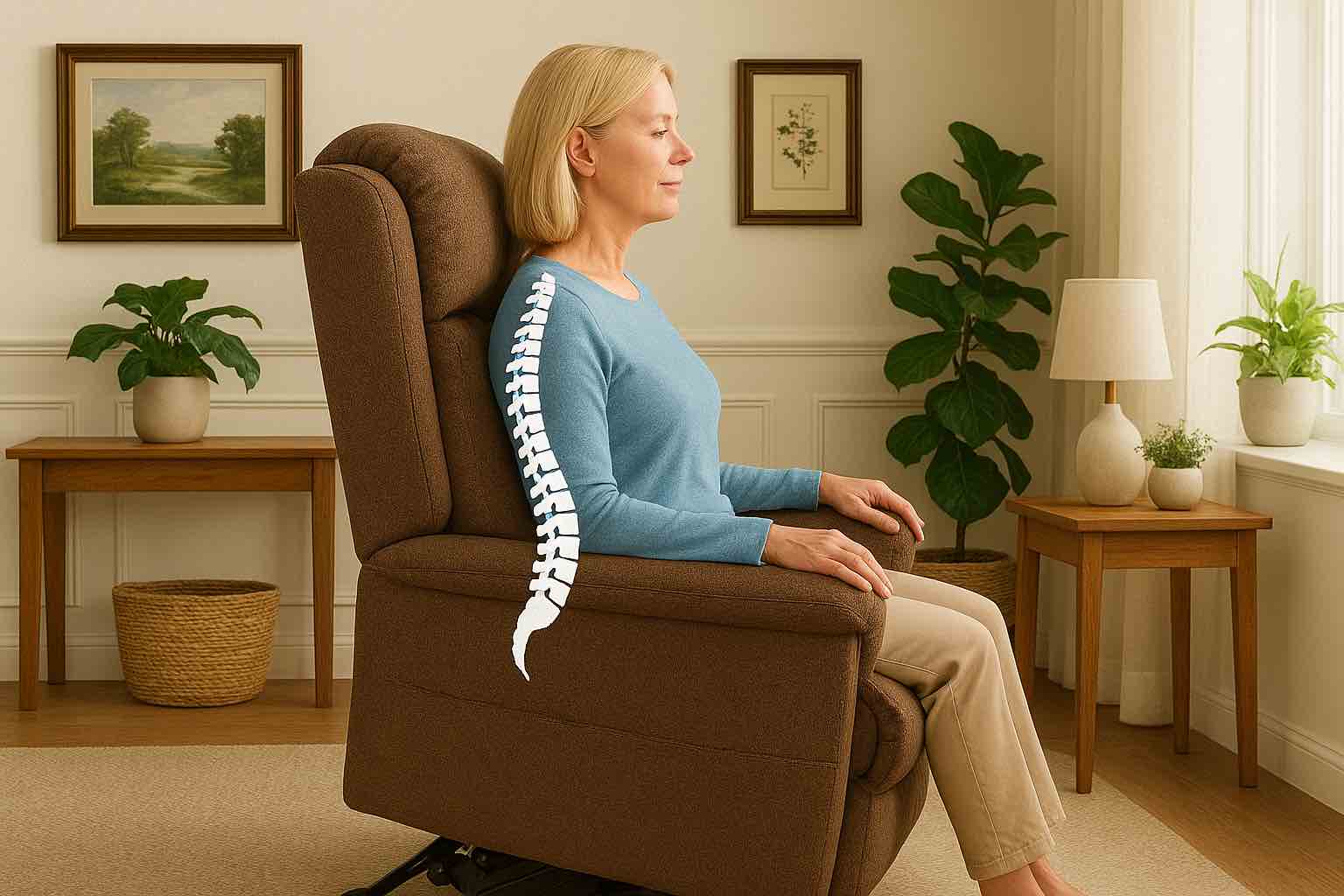
An anatomical guide depicting the best seated posture to relieve SI joint pain by aligning the spine, supporting the lumbar area, and positioning hips and feet correctly.
The Foundation of Good Posture: Understanding Spinal Alignment
The human spine naturally maintains an S-shaped curve when properly aligned, consisting of four distinct regions: cervical, thoracic, lumbar, and sacral. Maintaining these natural curves while seated is crucial for distributing weight evenly and preventing undue stress on any single area of the spine.3456
When we sit, the pressure within lumbar discs increases approximately 30% compared to standing. This increased pressure, combined with our natural tendency to slouch while working at desks, creates significant strain on the lower back and surrounding structures. Poor posture can lead to posterior pelvic tilt, where individuals sit on their sacrum rather than their ischial tuberosities, creating uneven pressure distribution and potential skin integrity issues.4567

Comparison of bad and good sitting posture showing the impact of neck and back alignment while using a phone in a chair.
Understanding Pressure Points and Skin Protection
The body has several vulnerable areas where pressure ulcers commonly develop, particularly the ischial tuberosities (sitting bones), sacrum, and coccyx. These bony prominences bear significant weight during sitting and are at highest risk for developing pressure sores when adequate pressure redistribution is not provided.28910
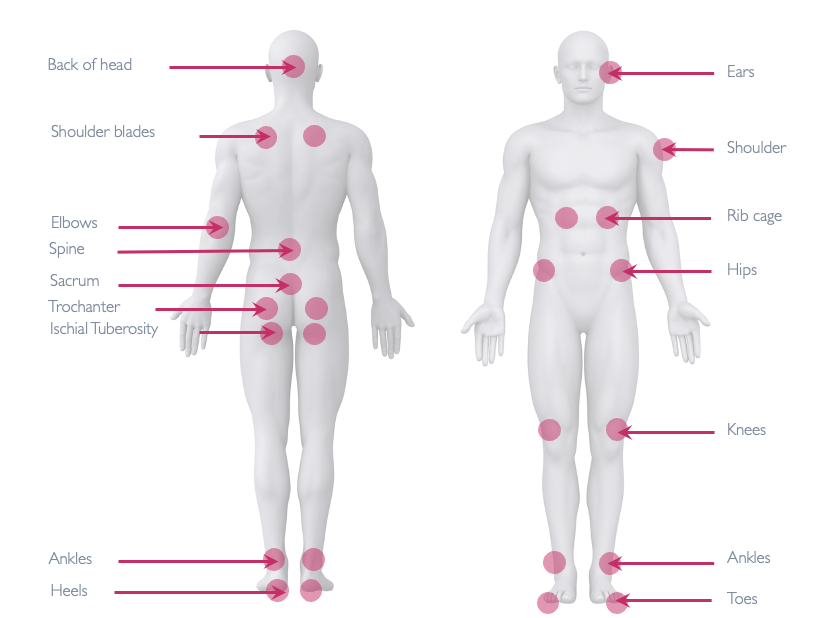
Anatomical diagram highlighting common pressure points vulnerable to pressure ulcers, essential for understanding pressure care in seating choices.
Research demonstrates that skin protection cushions significantly reduce pressure ulcer incidence. A clinical trial involving 232 nursing home residents found that specialized pressure-relieving cushions reduced ischial tuberosity ulcers from 6.7% to just 0.9% compared to standard foam cushions. This dramatic reduction highlights the critical importance of appropriate seating surfaces for maintaining skin integrity.2
Key Features of Protective Seating
Lumbar Support Systems
Effective lumbar support maintains the spine’s natural inward curve and prevents the flattening that occurs with prolonged sitting. Quality lumbar support should:1411
- Provide adjustable positioning to match individual spinal curves
- Offer firm but comfortable support at the L3-L5 vertebral level
- Allow for proper pelvic positioning with hips level or slightly higher than knees5

Ergonomic lumbar support cushion helps relieve spinal pressure, correct posture, ease muscle tension, and contour to the body.
Pressure Distribution Materials
Modern pressure-relieving cushions utilize various technologies to distribute weight and reduce pressure points:
Memory Foam and Visco-Elastic Materials: These materials conform to body contours, allowing bony prominences to sink while supporting surrounding tissue. High-density foam with castellated (egg-crate) surfaces further reduces friction and enhances pressure distribution.9101213
Gel Inserts: Gel-based cushions provide excellent pressure redistribution and can adapt to body temperature, though they may become firm in cold conditions.101415
Air Technology: Alternating pressure air cushions and static air systems offer superior pressure relief for high-risk individuals. These systems can provide dry flotation technology that delivers exceptional pressure redistribution.1314

Comparison of wheelchair cushions showing PURAP cushions outperform memory foam and gel in reducing pressure points and average pressure to protect the back, hips, and skin.
Seat Geometry and Adjustability
Proper seat dimensions are crucial for maintaining healthy posture and pressure distribution:
- Seat height should allow feet to rest flat on the floor with thighs parallel to the ground
- Seat depth must accommodate individual leg length without creating pressure behind the knees
- Seat angle should promote slight forward pelvic tilt to maintain lumbar lordosis45
Specialized Seating Solutions
For High-Risk Individuals
People with limited mobility, existing pressure injuries, or conditions affecting circulation require specialized seating interventions. Posture support care chairs with tilt-in-space functionality allow for pressure redistribution throughout the day while maintaining proper alignment.916
These chairs typically feature:
- Adjustable seat depth, width, and height
- Integral pressure relief in all contact surfaces
- Battery-powered position changes for pressure relief
- Specialized cushioning systems matched to individual risk levels16
Workplace Ergonomics
Office workers benefit from adjustable ergonomic chairs that accommodate prolonged sitting periods. Research shows that workplace chair interventions consistently reduce musculoskeletal symptoms, with the greatest improvements seen in neck, shoulder, and back pain.3417
Essential workplace seating features include:
- Height adjustability to maintain 90-degree elbow angles
- Proper lumbar support positioning
- Armrest adjustability to reduce shoulder strain
- Seat pan design that doesn’t restrict circulation4
Assessment and Selection Criteria
Professional Seating Assessment
A comprehensive seating assessment should evaluate:181920
- Pelvic positioning and identification of tilts or obliquities
- Spinal alignment including presence of kyphosis, lordosis, or scoliosis
- Joint flexibility and range of motion limitations
- Skin integrity and pressure ulcer risk factors
- Functional requirements and activity needs
Material Considerations
When selecting seating materials for pressure care, consider:1021
- Breathability to manage heat and moisture
- Antimicrobial properties for hygiene maintenance
- Washability for easy cleaning and infection control
- Durability to maintain pressure-relieving properties over time
Implementation Strategies
Progressive Positioning
For individuals transitioning to new seating systems, gradual adaptation is important. Start with shorter sitting periods and progressively increase duration as tolerance builds. This approach helps prevent discomfort while allowing the body to adapt to improved positioning.5
Regular Assessment and Adjustment
Seating needs can change over time due to:
- Changes in mobility or function
- Weight fluctuations
- Development of contractures or deformities
- Healing or progression of existing conditions1620
Regular reassessment ensures continued effectiveness of pressure care interventions and optimal postural support.
Conclusion
Effective posture and pressure care through appropriate seat selection represents a critical investment in long-term health and well-being. The evidence clearly demonstrates that proper seating can significantly reduce pressure ulcer risk while improving comfort and function. Whether addressing workplace ergonomics, managing high-risk medical conditions, or simply promoting daily comfort, understanding the principles of supportive seating empowers individuals to make informed choices that protect their back, hips, and skin integrity.217
The key lies in recognizing that one size does not fit all—successful seating solutions require individual assessment, appropriate material selection, and ongoing monitoring to ensure continued effectiveness in maintaining health and preventing complications.
https://www.hslchairs.com/feel-good-hub/wellness/how-to-choose-the-best-chair-for-back-pain ↩︎ ↩︎
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3065866/ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎
https://theadvancedspinecenter.com/the-ergonomic-approach-designing-your-workspace-for-spine-health/ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎
https://www.posturite.co.uk/posture-supports/lumbar-support-back-cushions ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎
https://www.essentialaids.com/comfort/pressure-relief-cushions.html ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎
https://www.spine-health.com/wellness/ergonomics/office-chair-how-reduce-back-pain ↩︎ ↩︎
https://www.independentlivingcentre.org.uk/buying-guide/posture-support-care-chair/ ↩︎ ↩︎
https://www.medicalsupplies.co.uk/wheelchair-pressure-relief-cushions.html ↩︎
https://www.cuh.nhs.uk/patient-information/seating-and-ergonomics/ ↩︎
https://www.invacare.co.uk/pressure-care-seating/matrx-backs/invacare-matrx-posture-back ↩︎
https://www.wheelfreedom.com/information-centre/pressure-care-and-cushions ↩︎ ↩︎
https://www.directhealthcaregroup.com/app/uploads/C22285-Practical-Guide-to-Specialist-Seating-Assessments.compressed.pdf ↩︎
https://mobilityfurniturecompany.co.uk/blog/product-guides/the-role-of-assisted-chairs-in-pressure-ulcer-prevention/ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎
https://sumedinternational.com/product/integrity-static-pressure-cushions-very-high-risk/ ↩︎ ↩︎
https://aci.health.nsw.gov.au/networks/spinal-cord-injury/spinal-seating/module-3/the-mechanical-assessment-tool-mat ↩︎
https://www.vivid.care/insights/advice-tips/best-cushions-for-pressure-sores/ ↩︎
https://www.hospitalbeds.co.uk/stimulite-classic-xs-pressure-relief-wheelchair-cushion.html ↩︎ ↩︎
https://seatingmatters.com/gb-ie/resources/importance-of-good-posture ↩︎
https://www.medirite.co.uk/healthcare-equipment/seating-wheelchairs/pressure-relieving-cushions ↩︎
https://www.sunrisemedical.eu/seating/jay/wheelchair-cushions ↩︎
https://healingtouchrehab.co.uk/postural-care-and-seating-assessment/ ↩︎